For twenty years, the internet ran on "Search Engines." The mechanism was simple: crawl, index, and rank based on popularity (backlinks).
In 2026, we have entered the era of the Generative Engine. Platforms like Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and SearchGPT do not just find information; they read it, understand it, and synthesize it into a new, unique answer.
This shift forces marketers to ask a fundamental question: What is a generative engine, and how does it select sources for AI-generated answers?
Why does Perplexity cite Forbes for one query but a niche Reddit thread for another? Why does ChatGPT trust your competitor's pricing page but ignore yours?
The answer lies in the complex architecture of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). It is no longer about "keywords"; it is about "semantic proximity" and "information gain."
In this technical guide, we will look under the hood of generative engines to understand their selection logic, ensuring your brand becomes a chosen source in the age of AI.
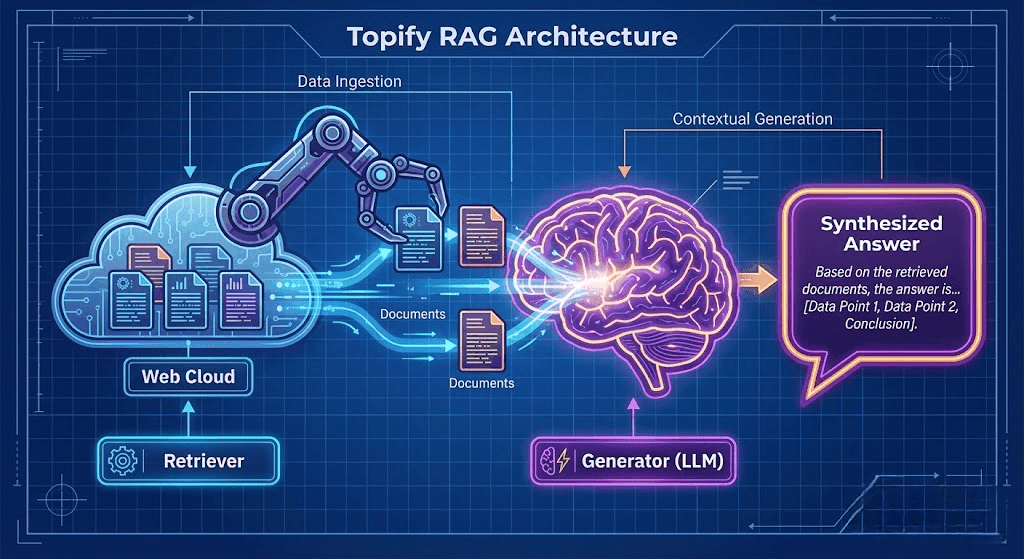
Defining the Generative Engine Architecture
To optimize for it, you must define it. A generative engine is not simply a chatbot. It is a hybrid system that marries two distinct technologies:
The Retriever (The Librarian): Scans the live web or a vector database to find relevant documents. This is similar to a traditional search engine but uses "Semantic Search" rather than just keyword matching.
The Generator (The Author): An LLM (like GPT-4 or Gemini) that reads the retrieved documents and synthesizes an answer.
How It Differs from Search: A search engine stops after the "Retrieval" phase. It gives you the list. A generative engine continues to the "Synthesis" phase. It selects specific sentences from that list to construct a narrative.
For a deeper comparison, read our breakdown of GEO vs SEO differences.
The RAG Workflow: How Sources Are Selected
When a user asks a question like "What is the best CRM for fintech?", the generative engine goes through a millisecond-by-millisecond decision process to select its sources.
Step 1: Semantic Query Analysis
The engine translates the user's natural language into a Vector Embedding—a mathematical representation of the intent behind the words. It doesn't just look for the string "CRM"; it looks for concepts related to "security," "compliance," and "financial data handling."
Step 2: Vector Similarity Retrieval
The engine scans its index for content that is mathematically close to that vector.
Selection Criteria: It prioritizes content with high Semantic Density. If your page talks about "growing your business" (vague), it has a weak vector match. If your page talks about "SOC2 compliance and bank-level encryption" (specific), it has a strong vector match.
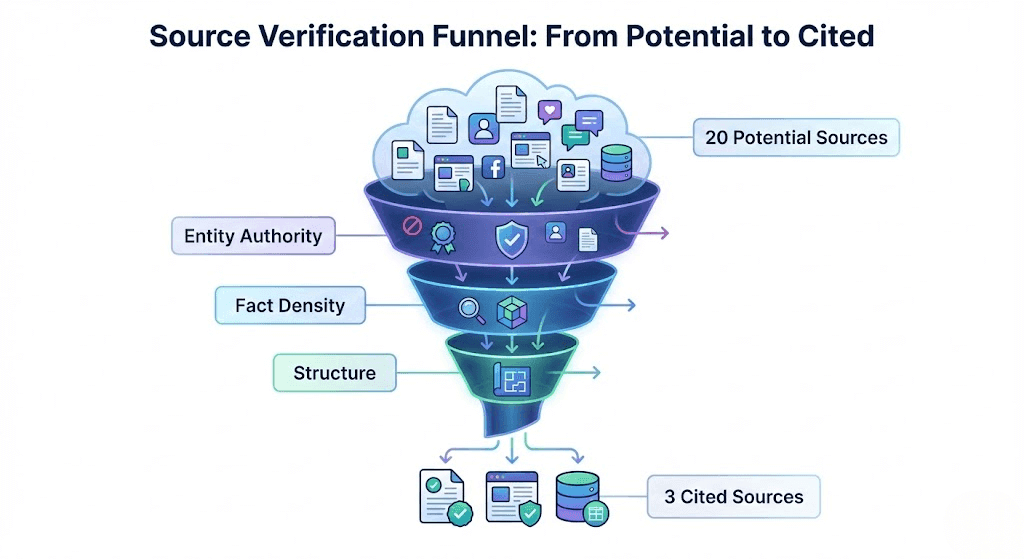
Step 3: The Re-Ranking Phase (The Filter)
This is where most brands fail. The engine retrieves perhaps 20 potential sources, but it can only read 3-5 to generate the answer. It applies a Re-Ranking Algorithm based on:
Entity Authority: Is this domain a known expert on this topic?
Information Gain: Does this source provide unique facts that the other 19 sources do not?
Freshness: Is the data current?
Step 4: Synthesis and Citation
The LLM reads the top 3-5 re-ranked sources. If it uses a specific fact from your page to construct a sentence, it appends a citation (footnote).
Critical Factors for Source Selection in AI
Understanding the RAG workflow reveals the specific levers marketers can pull to increase their selection probability.
Entity Authority and Trustworthiness
Generative engines rely on a "Knowledge Graph." If your brand is an unknown entity, the Re-Ranker will discard you in favor of a known quantity (like Gartner or G2). Optimization Strategy: You must build "Co-occurrence." Ensure your brand name appears alongside industry keywords on authoritative third-party sites. This trains the engine to associate your Entity with the Topic.
Structural Readability for Machines
Even if your content is relevant, it might be rejected if the LLM cannot parse it. Optimization Strategy: Use Semantic HTML.
Use
<table>tags for comparisons.Use
<ul>tags for features.Use
JSON-LDschema to explicitly define entities. Tools like Topify include a Content Generation feature that creates these machine-readable assets automatically.
High Information Gain and Fact Density
The engine wants to construct the most complete answer possible. It selects sources that provide unique tokens. Optimization Strategy: Audit your content for "Fact Density." Replace generic adjectives with specific numbers, dates, and proper nouns. Learn more about this concept in our guide on what is a generative engine optimization tool.
Using Topify to Audit Source Selection
How do you know if you are being selected? And if not, who is?
Topify provides a "Source Analysis" dashboard that reverse-engineers the selection process.
The Citation Audit: Topify tracks high-value prompts (e.g., "Best Enterprise Software") and lists every domain cited in the answer.
The Gap Analysis: It compares your content against the selected sources.
Did the winner have a better schema?
Did the winner mention a specific regulation you missed?
The Hallucination Check: Sometimes, an engine selects a source but misinterprets it. Topify's hallucination detection ensures that when you are selected, the information presented is accurate.
Read more about tracking mechanisms in how to monitor brand visibility in AI.
Comparison: Search Engine Indexing vs. Generative Engine Selection
To clarify the difference between "Ranking" and "Selection," here is a technical comparison.
Feature | Search Engine (Google) | Generative Engine (Perplexity/GPT) |
Primary Goal | Indexing & Ranking Links | Retrieving & Synthesizing Facts |
Selection Logic | Keyword Matching & Backlinks | Vector Similarity & Fact Density |
User Output | 10 Blue Links | 1 Coherent Answer |
Authority Signal | Domain Authority (DA) | Entity Salience |
Data Usage | Metadata (Title/Desc) | Full Text Body Content |
Evaluation Tool | Google Search Console | Topify |
Optimizing for Specific Generative Engines
Different engines have different selection biases.
ChatGPT (The Knowledge Engine):
Bias: Favors established, long-term "World Knowledge."
Strategy: Focus on updating Wikis, Crunchbase, and getting into major industry reports to become part of the training data.
Perplexity (The News Engine):
Bias: Favors Recency and Citation count.
Strategy: Digital PR. Publish timely reports and press releases that get syndicated quickly.
Google AI Overviews (The Hybrid):
Bias: Favors content that directly answers the query (Direct Answer formatting).
Strategy: Place 40-word definitions at the top of your H2s.
For a review of tools that track these distinctions, see best AI search visibility tools.
The Future of Source Selection: Agentic Validity
As we look toward 2027, generative engines will evolve into "Agents." They won't just answer questions; they will perform tasks (e.g., "Book me a flight").
In this future, "Source Selection" becomes "Service Selection." The engine will select the source that is not only informational but API-ready and transactional.
Brands that structure their data today using tools like Topify are laying the groundwork for this agentic future.
Conclusion: Becoming the Chosen Source
The question "What is a generative engine and how does it select sources?" is the most important inquiry for modern SEOs.
The answer is clear: It selects sources that are authoritative, dense with facts, and structured for machines.
You can no longer rely on keyword stuffing. You must optimize your Entity. By using platforms like Topify to audit your presence and restructure your data, you ensure that when the AI synthesizes an answer, your brand is the foundation it builds upon.
Start measuring your AI Share of Voice today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Generative Engines
Q1: What is a generative engine?
A generative engine is an AI system that retrieves information from the web (or a database) and uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to synthesize a direct answer, rather than just listing links.
Q2: How does an AI decide which source to cite?
It uses a process called RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). It converts the query into vectors, finds semantically similar content, re-ranks it based on authority and information gain, and cites the top results.
Q3: Can Topify help me get selected as a source?
Yes. Topify analyzes the sources that are currently winning citations and helps you optimize your content's structure and fact density to beat them in the Re-Ranking phase.
Q4: Is Domain Authority (DA) still important?
Yes, but "Entity Authority" is more important. A site with lower DA can beat a high DA site in Generative Search if it has higher "Vector Similarity" and specific facts relevant to the query.
Q5: Why does Perplexity cite Reddit so often?
Because generative engines prioritize "Human Nuance" and "Consensus." Reddit threads often contain high-density, authentic user experiences that LLMs are trained to value over marketing fluff.


